Egypt came first, then history and civilization came. Egypt has one of the world's seven wonders of the pyramids. The Virgin Mary came to protect herself and her son. Egypt is the safest destination for tourism. My goal is to help foreigners learn my country’s history, come to Egypt, whatever your budget, and I will be your guide at no additional cost to you. booking with us. The goal is to service booking tours to Egypt. the best Nile cruise in Egypt. https://kingofegypttours.com
Sunday, 19 July 2020
Imhotep: the God of Wisdom and Medicine Who Built the First Pyramid
.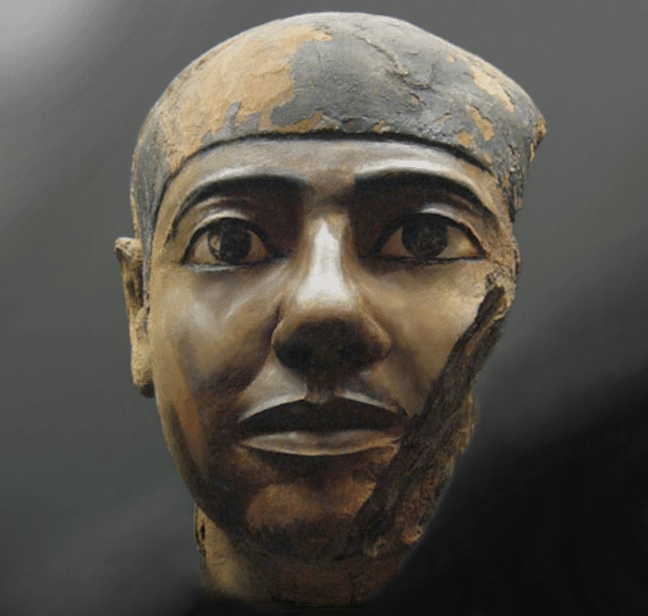
Imhotep is a Greek word meaning ‘he that comes in peace’. Born in the 27th century, Egypt, Imhotep was no only a physician but also an architect, astrologer, scribe, politician and priest.
He is a renowned scholar and contributed greatly to Egypt’s civilization. Apart from Amenhotep, he is the only other Egyptian to be deified. As a vizier, it was his duty to oversee everything in the land and only the finest educated could hold that position.
Imhotep, the first doctor in history.
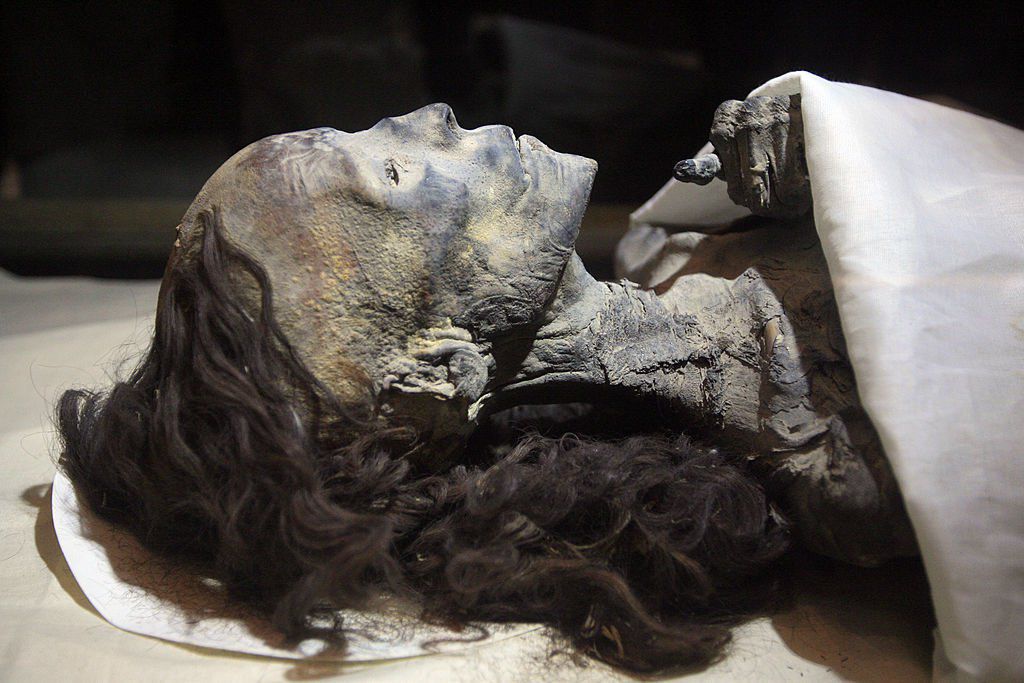
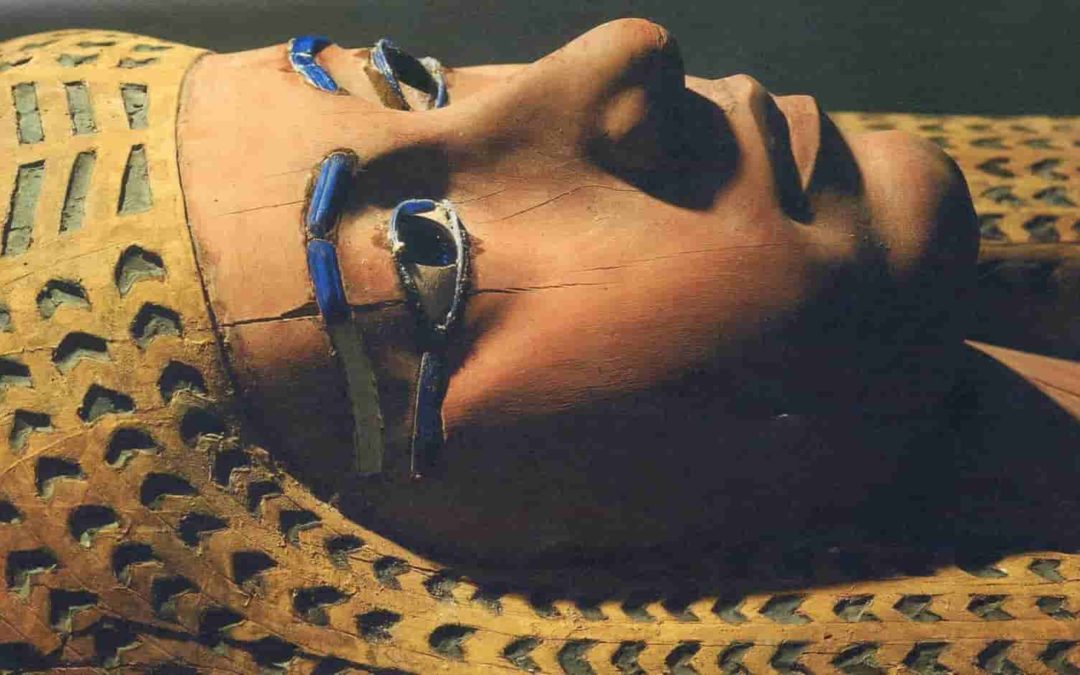
The Many Layers of an Egyptian Mummy.
The Many Layers of an Egyptian Mummy
Mummification was not the final step in the quest for eternal life. The body would be placed in several cases and coffins, sometimes up to eight, before eventually being laid to rest.
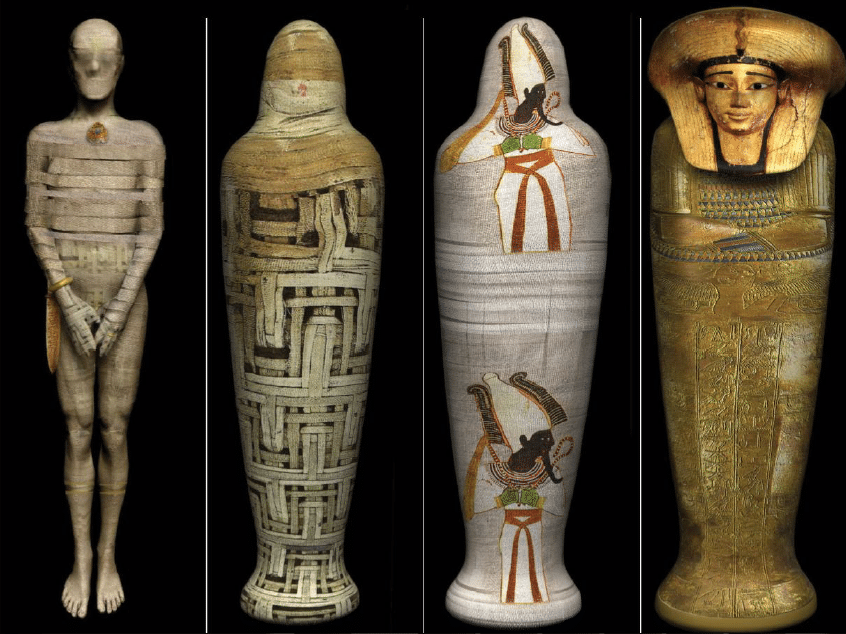

1 – Objects for the afterlife
Once the body had been wrapped in layers of linen, items like jewellery and daggers were placed on the mummy for use in the afterlife.
A scarab amulet was hung from the neck to help guide the soul during the Weighing of the Heart ceremony.
2 – Cartonnage Case
After mummification, a cartonnage case was created. This was formed around a straw and mud core, to which plaster and linen bandages soaked in resin or animal glue were applied, similar to papier-mache.
Once it set, the case was split open, the stuffing removed and the body placed inside.
3 – Decoration
Another cartonnage case was added and then a layer of plaster or gesso, made from resin and chalk powder, was painted over the top.
Natural dyes like indigo, madder and ochre were used to create intricate designs on the cartonnage, particularly depictions of the god of the underworld, Osiris.
4 – Wooden Coffin
The body was placed in an anthropoid wooden coffin. Those of royalty may have been painted with gold leaf and decorated with precious jewels.
A death mask made of cartonnage, wood or precious metals was placed on the head to ensure that its soul could recognize its body.
Eye of Horus magic.

In the form of an amulet, it was one of the most powerful and important and the amount of copies that were taken or included in the mummy increased its protective value.
It served to counteract the effects of the evil eye, as a remedy against eye diseases and to protect the deceased from any harmful enchantment or bad luck, enhancing the vision, both real and introspective.
Why Were Cats So Important In Ancient Egypt?








On many occasions, we have observed that cats in ancient Egypt, specifically in the New Kingdom (1550-1069 BC), were animals venerated by the inhabitants themselves.
This arises for two reasons: the first, due to the worship of the gods. The second, the cat as a domestic animal, both connected to each other.
Starting with the first, we find the gods Ra and Bastet. In the ancient Egyptian religion, Bastet is the personification of the warm rays of the sun.
She is represented as a woman with a cat’s head or an entire cat and defended Ra, the god of the Sun, against the attacks of the Apophis snake.
A very clear example of this scene is found in the tomb of Inherkhau. It is necessary to mention that also Ra, in some old myths, adopted the form of a cat to descend to earth.
In the New Kingdom, the cat was considered an incarnation of the Sun god and the manifestation of the goddess Bastet. The ancient Egyptians sought to seek the happiness of the goddess, who symbolized the power of the sun, the protection of the home and the joy of living.
This brings us to the second reason, what did the cats in ancient Egypt do?
It is believed that domestication began during the 3rd millennium B C. The cat became a companion animal appreciated for its sweetness, charm, its mysterious behaviour, and above all, for being protective of the home.
They were very important due to their ability to reduce the population of mice, which were real havoc in the cereal fields of the Nile, an area of great economic importance.
In addition, cats in ancient Egypt kept the houses clean because when hunting rats and snakes, a carrier of serious diseases was eliminated, as the plague and the surroundings of nearby homes were safer.
The cat achieved importance that was increasing over the years, both religiously and socially. In the New Kingdom, the cat is trained to take it to bird hunting.
The ancient Egyptians had great respect for their cats’ lives. The members of the family held a funeral when their cat died. They shaved their eyebrows as a sign of affliction and mourning, and if they had the necessary resources, the cat was embalmed in a special sarcophagus.
The cat was transported to the city of Bubastis, to be buried with solemnity and figures in the shape of a cat were placed as an offering to obtain the favour of the goddess Bastet.
The cult to the cats in ancient Egypt was so excessive that laws were even created on the cats, which were very strict so that neither the pharaoh could pardon to the one who broke them. This can be seen in texts by some Greek historians.
Diodorus Siculus tells how the crowd of Alexandria was launched against a Roman citizen who had accidentally killed a cat and asked for the death penalty for him.
Herodotus explains anecdotes in case of fire and the laws applied to cats:
“When a fire is declared, it’s amazing what happens with cats, people stay at a certain distance taking care of the cats and without worrying in the least to put out the fire, but the cats slip through the crowd or jump over their heads and rush into the fire, and when this happens, the Egyptians get very sorry”
“If someone voluntarily kills one of these animals, he is condemned to death and if he does so involuntarily, he pays a fine fixed in each case by the priests …”
Ctesias speaks of the Battle of Pelusium (525 BC), in which the Persian king Cambyses II and the pharaoh of Egypt, Psametik III, fought. It is said that the Persians devised a stratagem to defeat using on their shields representations of the goddess Bastet and capturing cats to release them during the battle and make the Egyptians fight carefully so as not to harm the cats.
After the battle, the Egyptians took refuge in Peluso. When they besieged the city, Cambyses II continued to use the felines in his favour. The soldiers threw the cats towards the fortress and forced the Egyptian archers to shoot with caution.
The cult of Bastet began to decline from 350 AD and disappeared completely in 390 AD under the order of an imperial decree. There are, however, many mural paintings that relate to the different stages of cat life in ancient Egyptian society.
In 1890 in the Egyptian village of Tell-Basta, the ancient Bubastis, archaeologists discovered an ancient cemetery in which three hundred thousand mummies of mummified cats were counted and placed each in a small coffin that represented the shape of the animal.
Apparently, the priests got to mount a lucrative business around the sale of mummified cats, since many inhabitants considered an honour to be buried next to mummified cats, even the pharaohs.
Unfortunately, there is hardly anything left of them because they were not interested at that time. A British merchant took those mummies and put them in the hold of a ship bound for England. He crushed them and sold them as fertilizer to farmers in the port of Liverpool. Only a few were saved from that.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
GOOD MORNING FROM EGYPT EGYPT READY NOW مصر مستنياك
GOOD MORNING FROM EGYPT EGYPT READY NOW مصر مستنياك http://kingofegypttours.com/ Egipto te espera http://kingofegypttours.com/ Egypt is wa...

-
Cairo is fan-shaped, narrowest in the south, where the river valley is wedged between desert escarpments, and widest in the north, where t...
-
GOOD MORNING FROM EGYPT EGYPT READY NOW مصر مستنياك http://kingofegypttours.com/ Egipto te espera http://kingofegypttours.com/ Egypt is wa...
-
The Coffer inside the King’s Chamber is made of a solid block of granite. Curiously, despite the fact that the Pyramid is tough to have ...